We all hear of certain rules in photography that one may want to abide by. It is not to say these rules are set in stone but if followed, normally your photos stand out that much more.

![]()
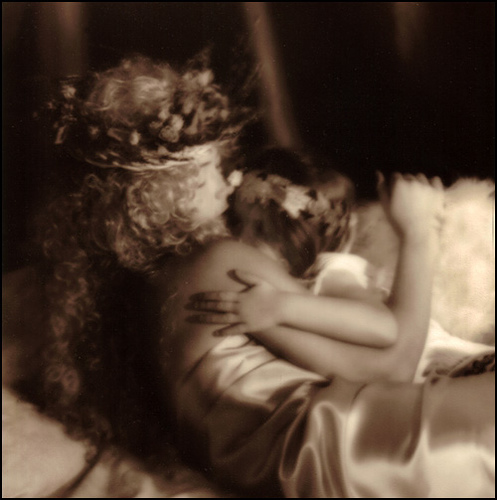
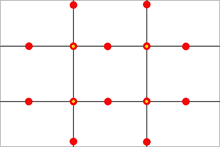
The ‘Rule of Thirds’ is used regularly by most advanced photographers. The rule states that an image should be imagined as divided into nine equal parts (like a tick tack toe board) by two equally-spaced horizontal lines and two equally-spaced vertical lines, and that important compositional elements should be placed along these lines or their intersections. The shot above is a good example. Most newbies would have placed the model dead center in this image. The image works much better compositionally with the model to to right of center on one of the lines with the yellow dot. Play with this ‘rule’ for yourself just to test it out.
Depth of Field (otherwise known as DOF), is the area from the foreground to the background within your photo that is in focus. A narrow DOF (F-2.0 or F-2.8 for example) will allow the main subject of your photo in be in focus while the background is blurred. A wider DOF allows one’s eyes to wander over the whole image as there are more details that are in focus.
Other ‘rules’ to consider include leading lines, framing, foreground interest and more.
Original link from our Photography forum










